Monitoring custom log directories using sidecar container in Kubernetes
Purpose: Monitoring custom log directories in Kubernetes deployments.
Explanation:
- Some applications write logs to custom directories that are not monitored by default Kubernetes logging mechanisms.
- This can lead to challenges in accessing and analyzing these logs, impacting troubleshooting efforts.Possible Solution :
- It involves creating a Kubernetes deployment that includes an initialization container to ensure the existence of the custom log directory and log files,
- A sidecar container responsible for monitoring the custom log directory.Source Code : github.com/vishalk17/logs-capturing-sidecar..
Initialization Container:
An initialization container will be added to the pod to ensure that the custom log directory and log files exist.
This ensures that the sidecar container has access to the log files for monitoring.
initContainers:
- name: create-log-directory
image: busybox:latest
command: ["sh", "-c", "mkdir -p /var/custom && touch /var/custom/app-custom.log"]
volumeMounts:
- name: log-volume
mountPath: /var/custom # shared volume
Log Monitoring with Sidecar Container:
The sidecar container will be configured to continuously monitor the custom log directory and tail the log files using tool like
tail.This ensures that all log events are captured in real-time, regardless of the logging mechanism used by the application.
containers:
- name: nginx # testing purpose only
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: log-volume
mountPath: /var/custom # shared volume
- name: log-tailer # sidecar container Name
image: busybox:latest
# Command to prepend 'vishal-app' prefix to each line of the log file
command: ["sh", "-c", "tail -n +1 -F /var/custom/app-custom.log | awk '{print \"vishal-app\", $0}'"]
volumeMounts:
- name: log-volume
mountPath: /var/custom # shared volume
volumes:
- name: log-volume # volume same for all
emptyDir: {}
To improve log identification and categorization, we'll add prefix (vishal-app) to log lines based on the source application.
This will be achieved by modifying the sidecar container to prepend each log line with a unique identifier corresponding to the application generating the log.
Deploy manifest files in k8s
- touch nginx-sidecar.yaml
### Modified by github.com/vishalk17 , t.me/vishalk17
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-with-sidecar
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-with-sidecar
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-with-sidecar
spec:
initContainers:
- name: create-log-directory
image: busybox:latest
command: ["sh", "-c", "mkdir -p /var/custom && touch /var/custom/app-custom.log"]
volumeMounts:
- name: log-volume
mountPath: /var/custom
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: log-volume
mountPath: /var/custom
- name: log-tailer
image: busybox:latest
# Command to prepend 'vishal-app' prefix to each line of the log file
command: ["sh", "-c", "tail -n +1 -F /var/custom/app-custom.log | awk '{print \"vishal-app\", $0}'"]
volumeMounts:
- name: log-volume
mountPath: /var/custom
volumes:
- name: log-volume
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx-with-sidecar # This should match the labels in your Deployment
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP # You can change this to NodePort or LoadBalancer based on your requirements
kubectl apply -f nginx-sidecar.yaml
kubectl get pods
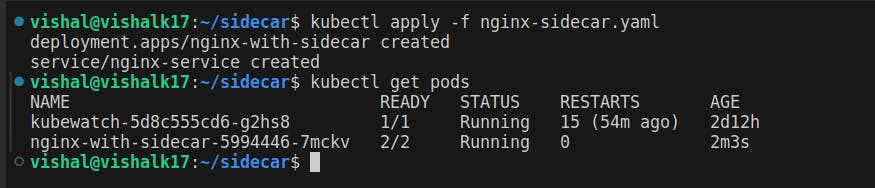
Testing
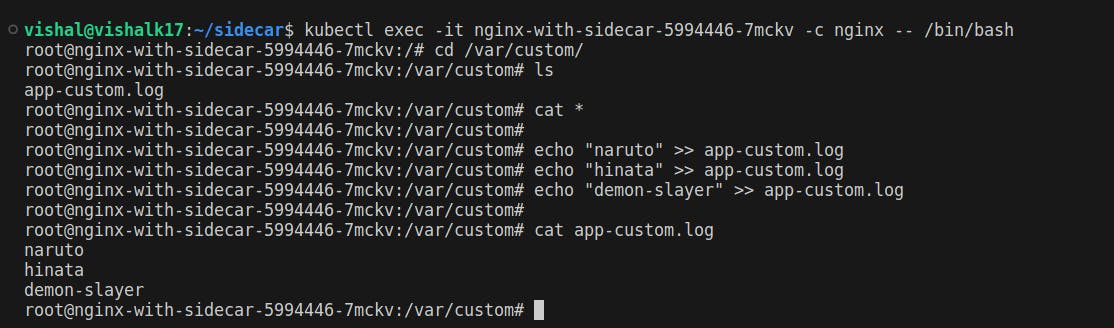
Enter in the container of the pod
Write some lines in file i.e., /var/custom/app-custom.log
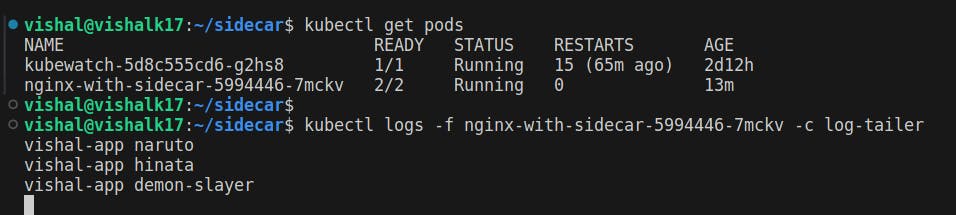
- Observing the logs using the 'kubectl logs' command
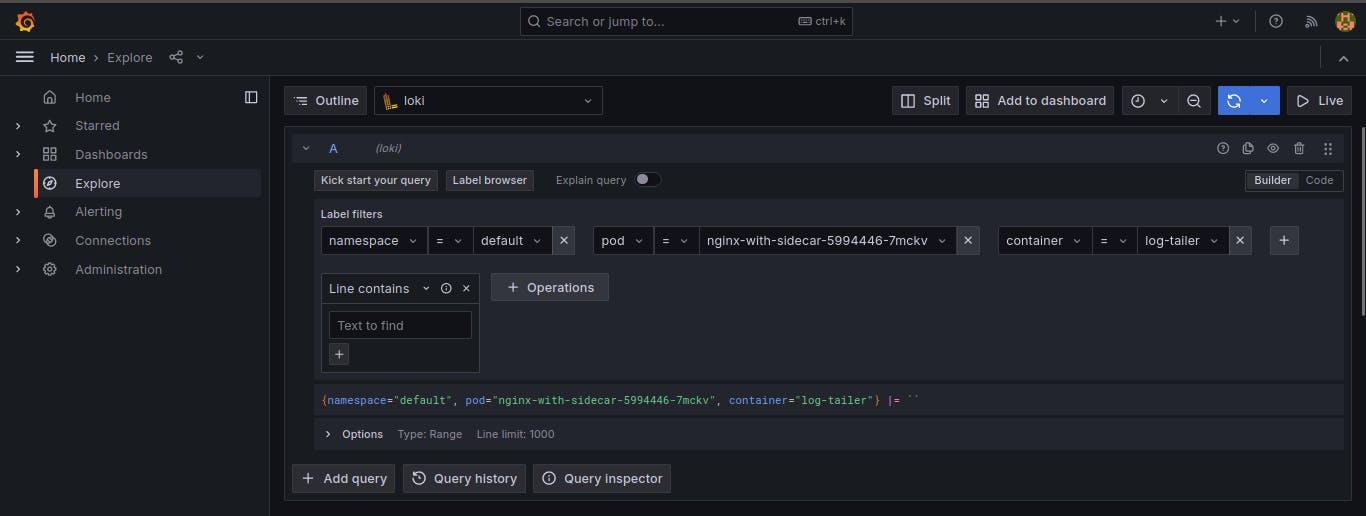
- Monitoring them in the centralized logging system in my case i m using ( loki - grafana - prometheus ).
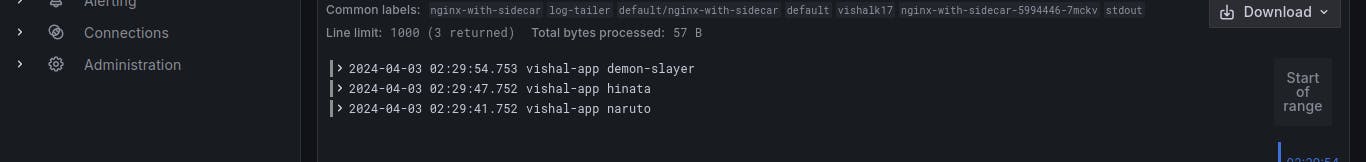
Done :)
